About NCRPB |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The National Capital Region Planning Board (NCRPB), constituted in 1985 under the provisions of NCRPB Act, 1985, is a statutory body functioning under the Ministry of Urban Development, Government of India. NCRPB has a mandate to systematically develop the National Capital Region (NCR) of India. Lying between 27o03’-29o29’ North latitude and 76o07’-78o29’ East longitude, the NCR spreads over an area of 33,578 sq. km. The constituent areas of the National Capital Region are:
In addition to the NCR, the NCRPB has also selected, in consultation with the respective state governments, following Counter Magnet Areas (CMA), considering their location, population and potential growth for implementing development programs, in order to achieve the objectives of the regional plan: (i) Gwalior (Madhya Pradesh State); (ii) Patiala (Punjab); (iii) Hissar (Haryana); (iv) Kota (Rajasthan); and (v) Bareilly (Uttar Pradesh). Area and Population. According to Census 2001, the total population of NCR is 37.1 million, housing in a total area of 33,578 sq. km, with an average gross density of 1,104 persons per sq. km. 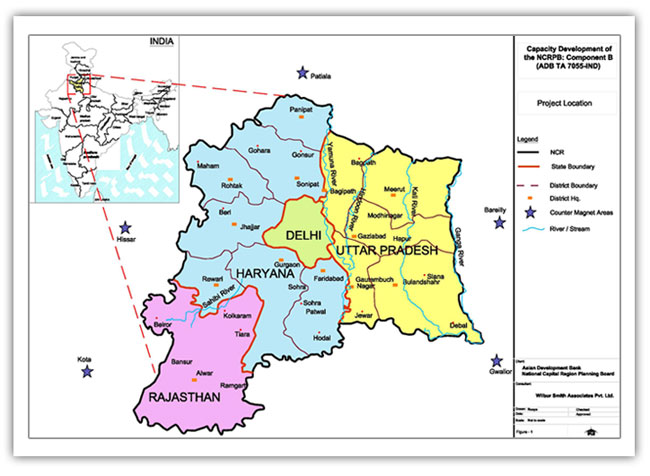
Table 1: Area and Population of NCR Constituents
NCRPB Act, 1985 stipulates various functions of the Board as under:
NCRPB has prepared regional plan for NCR area with the perspective year 2021. Further, the Board also initiated preparation of functional plans to elaborate one or more elements of the Regional Plan. Accordingly the study groups have been constituted for preparation of functional plans of drainage and power. Consultancy services have been awarded for water and transportation which would assist in preparation of functional plan for these sectors The NCRPB Act also defines the roles of State Governments/State NCR Cell, which includes the following:
As stated above, each participating State is required to prepare a sub-regional plan for the sub-region within the state. On request of Rajasthan and Haryana states the Project Sanctioning & Monitoring Group (PSMG) has allowed these states to outsource preparation of sub regional plan. The role of state departments, ULBs and agencies, which are primarily responsible for provision of basic services, include:
Project Financing by NCRPBAs defined by the NCRPB Act, one of the functions of the Board is to arrange and oversee the financing of selected development projects in the NCR through Central and State Plan funds and other sources of revenue. For this purpose NCRPB Fund has been created. Board may finance development projects implemented in national capital region (NCR) and counter magnet areas (CMAs), which are identified by Board, participating state governments and their implementing agencies including Urban Local Bodies (ULBs), Development Authorities (DAs), Housing Boards, Industrial Development Corporations or other agencies of the State governments. NCRPB gives significant emphasis for building water supply and sanitation infrastructure. The Board provides loan for a project up to 75 percent of the estimated cost and the balance needs to be contributed by the State Government and their Implementing Agency.Depending on the availability of resources, the following types of projects are considered for financing by the Board:
|



